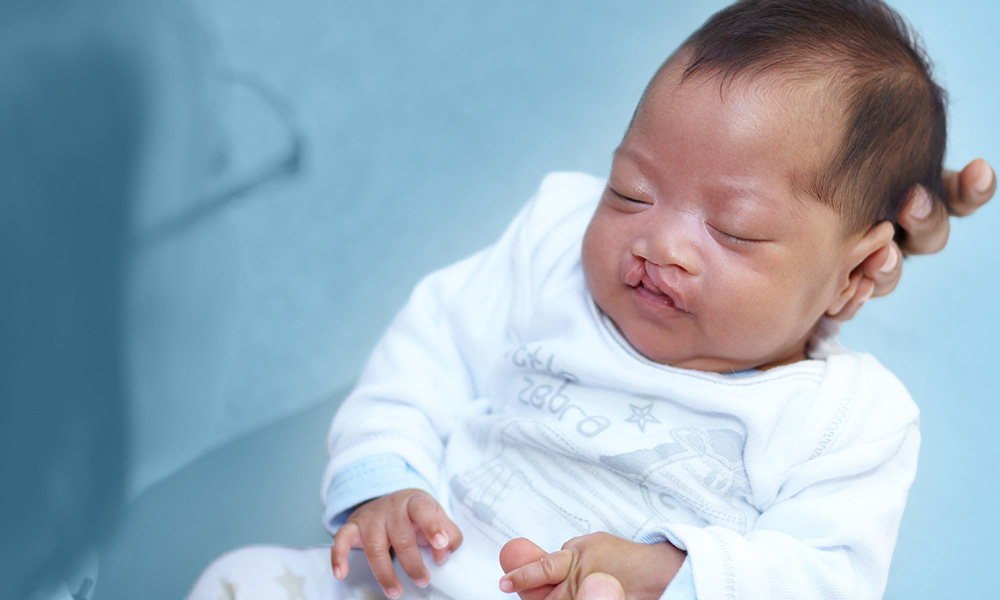
A cleft lip is a congenital deformity that occurs when the tissue in the lip fails to fuse properly during fetal development, resulting in a split or gap in the lip. It is one of the most common birth defects, affecting approximately 1 in 700 births worldwide.
In this article, the Houston dentist will help you delve into cleft lip, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies.
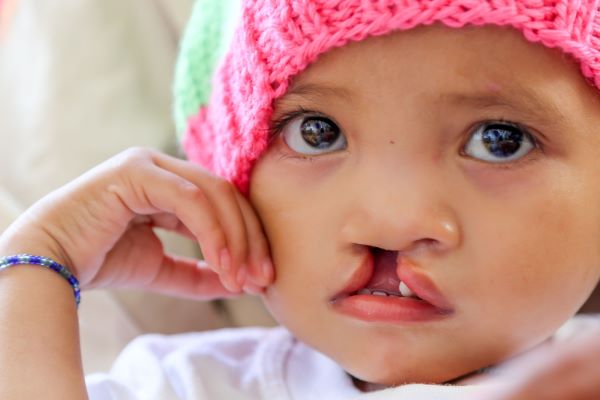
What causes a cleft lip?
The exact cause of cleft lip is unknown, but research suggests that it combines genetic and environmental factors. Some risk factors include:
- Family history
- Exposure to certain substances during pregnancy
- Older mother
- Certain medications are taken during pregnancy such as antiseizure, and anti-cancer drugs
Factors related to the birthing parent that can contribute to the development of cleft lip:
- Folic acid deficiency
- Obesity
- Smoking or other tobacco use
- Having substance use disorder
- Exposure to certain viruses and chemicals during pregnancy
What are the symptoms associated with cleft lip?
A cleft lip can present in different ways, including:
- A small notch in the lip
- A complete split in the lip that extends into the nose
- A split in the lip that affects the nose and palate
- Difficulty feeding
- Speech difficulties
- Hearing loss
How can a cleft lip be diagnosed?
A cleft lip is usually noticeable at birth and is typically diagnosed during a physical examination. In some cases, a cleft lip may not be diagnosed until later in life, during a speech or hearing evaluation.
How can a cleft lip be treated?
Treatment for a cleft lip typically involves a team of specialists, including a plastic surgeon, an oral surgeon, a speech therapist, and an orthodontist. The goal of treatment is to improve the appearance and function of the lip, as well as to address any related speech, hearing, or dental issues.
Surgery:
- Cleft lip repair: usually performed within the first few months of life
- Follow-up surgeries may be necessary to refine the appearance and function of the lip
Speech Therapy:
- To improve speech and communication skills
- To address any related speech or language disorders
Dental Care:
- To monitor and address any dental problems
- To ensure proper oral hygiene and care
Hearing Tests:
- To monitor and address any hearing loss or ear infections
What are the management strategies involved for cleft lip?
In addition to medical treatment, several management strategies can help individuals with a cleft lip, including:
Feeding strategies: using specialized equipment, such as the Haberman Feeder, to make feeding easier
Speech therapy: to improve communication skills
Dental care: to monitor and address any dental problems
Hearing tests: to monitor and address any hearing loss or ear infections
Psychological support: to address any related emotional or psychological issues
What dental care will a child with cleft lip need?
Children with cleft lips will have the same dental needs as other children. Some dental care recommendations include:
- Early dental care through good nutrition, proper teeth cleaning, and fluoride treatment for healthy teeth. Use a suitable soft-bristled toothbrush with low-fluoride toothpaste.
- Orthodontic care in the form of braces and orthognathic surgery may be required for proper teeth and jaw alignment.
- Prosthodontic care in the form of dental bridges to replace missing teeth.
Key takeaway
A cleft lip is a congenital deformity that can affect an individual’s speech, hearing, dental development, and overall quality of life. While the exact cause is unknown, research suggests that it combines genetic and environmental factors. With proper treatment and management, individuals with a cleft lip can lead normal and healthy lives. If you or someone you know has been affected by a cleft lip, seeking medical attention and working with a team of specialists is essential to develop a comprehensive treatment plan.










Comments